What Does Negative Price To Earnings Ratio Mean? A Deep Dive Into Its Implications
Ever wondered what it means when a company has a negative price to earnings ratio? Well, buckle up because we're diving headfirst into this financial rabbit hole. This isn't just some random number; it’s a key indicator that can tell you a lot about a company's health. So, let’s get started, shall we?
When you're scrolling through stock reports or chatting with your finance-savvy friends, you might hear someone drop the term "negative P/E ratio." At first glance, it sounds like bad news, right? But hold on a sec—there’s more to it than meets the eye. Understanding this concept is crucial if you're into investing or just curious about how businesses work.
Now, before we dive deeper, let me give you the lowdown. A negative price to earnings ratio doesn’t automatically mean the company is doomed. Sometimes, it’s just a phase. Other times, it might indicate some serious underlying issues. Stick around, and we’ll break it all down for you in a way that’s easy to digest.
- David And Rebecca Muir Wedding Love Story That Captured Hearts Worldwide
- Ullu Uncut The Hottest Buzzword In Entertainment Thats Got Everyone Talking
What Exactly is Price to Earnings Ratio?
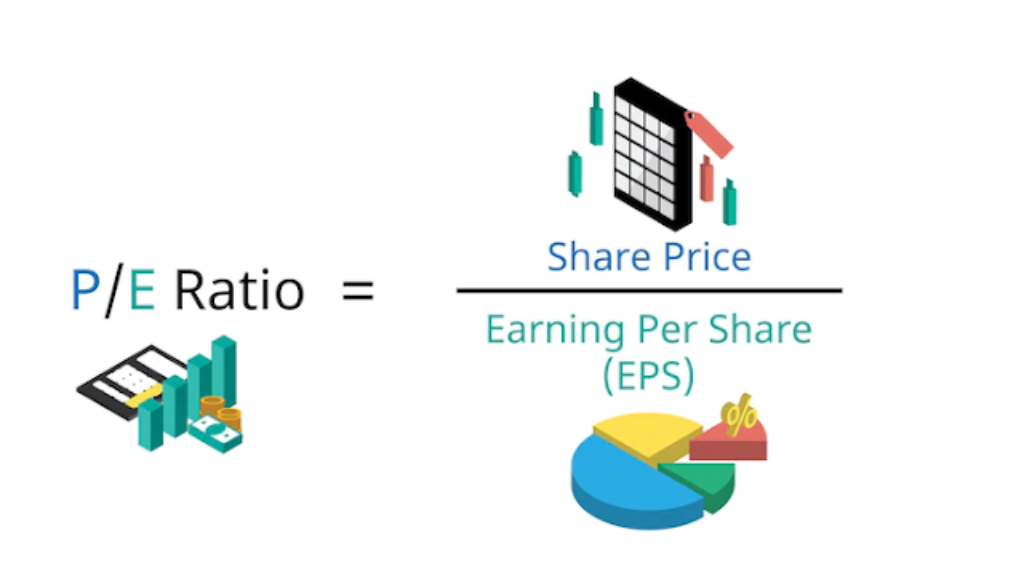
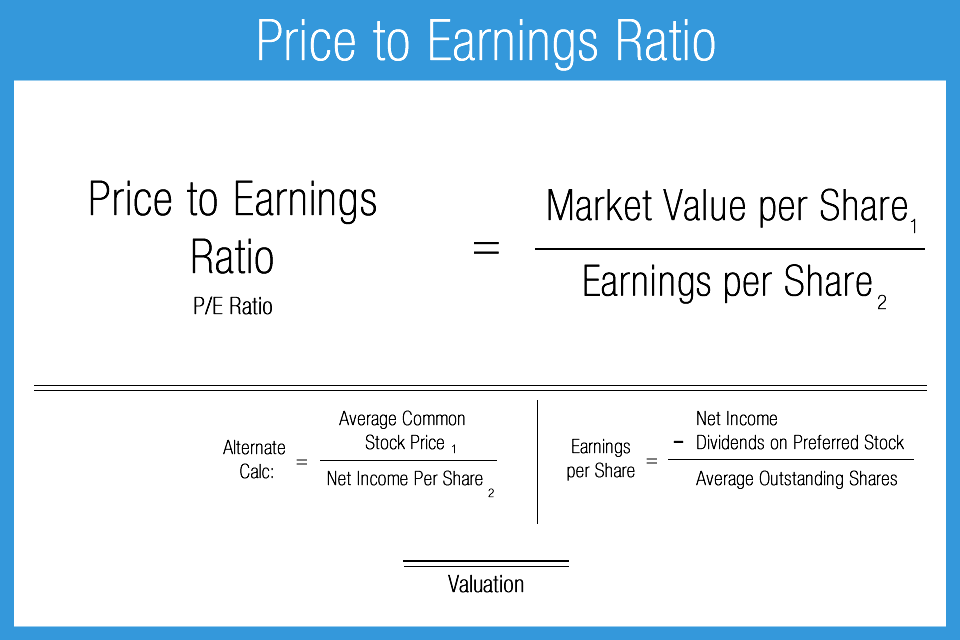
Alright, let’s start with the basics. The price to earnings ratio, or P/E ratio, is like the financial world’s version of a report card. It measures how much investors are willing to pay for every dollar of a company’s earnings. Think of it as a way to gauge whether a stock is overpriced or undervalued.
Here’s the formula for the P/E ratio: Stock Price ÷ Earnings Per Share (EPS). Simple, right? But here’s the twist—if a company’s earnings are negative, you end up with a negative P/E ratio. And that’s where things get interesting.
Now, why should you care? Well, the P/E ratio is one of the most widely used metrics in the investing world. It helps investors make informed decisions. But when it turns negative, it raises a bunch of questions that need answering.
- Paige Vanzant Leaked The Untold Story And What You Need To Know
- Drew Gulliver Onlyfans Your Ultimate Guide To The Creatorrsquos Rise And Content
Why Does a Negative P/E Ratio Happen?
Let’s face it—a negative P/E ratio isn’t exactly a badge of honor. But it’s not always a sign of disaster either. There are several reasons why a company might end up with this financial anomaly.
1. The Company is Losing Money: The most obvious reason is that the company isn’t making a profit. If earnings are negative, the P/E ratio automatically becomes negative too. This could happen due to poor management, market competition, or unexpected expenses.
2. One-Time Events: Sometimes, a company takes a hit because of a one-time event, like a lawsuit or a major recall. These events can temporarily skew the earnings, resulting in a negative P/E ratio.
3. Expansion Phase: Believe it or not, some companies intentionally operate at a loss during their early stages. They might be investing heavily in growth, which can lead to negative earnings in the short term. Think of tech startups or companies expanding into new markets.
Is a Negative P/E Ratio Always Bad?
Not necessarily. While a negative P/E ratio can be a red flag, it’s not always the end of the world. It all depends on the context. For example, if a company is in a high-growth phase and is reinvesting its profits into expansion, a negative P/E ratio might not be as alarming.
On the flip side, if the company has been consistently losing money for years, it could signal deeper issues. In such cases, investors need to dig deeper to understand the root cause.
How to Interpret a Negative P/E Ratio
Interpreting a negative P/E ratio requires a bit of detective work. Here are a few things to consider:
- Industry Trends: Some industries naturally have lower profit margins. For example, tech companies often operate at a loss during their early stages. Understanding industry norms can provide valuable context.
- Historical Performance: Look at the company’s past performance. Has it been profitable in the past? If so, the negative P/E ratio might just be a temporary blip.
- Management Strategy: Sometimes, companies intentionally operate at a loss to gain market share or develop new products. Understanding the company’s strategy can help you make a more informed decision.
Key Questions to Ask
When analyzing a negative P/E ratio, here are some key questions to ask:
- Is the company investing in growth?
- Are there any one-time events affecting earnings?
- What’s the long-term outlook for the company?
Real-World Examples of Negative P/E Ratios
To make things clearer, let’s look at a couple of real-world examples. These examples will help you understand how a negative P/E ratio plays out in the real world.
Example 1: Tesla
Tesla is a great example of a company that operated with a negative P/E ratio for years. During its early stages, Tesla was heavily investing in research and development, which led to negative earnings. However, investors were confident in the company’s long-term potential, and the stock price continued to rise.
Example 2: Amazon
Amazon is another company that spent years with a negative P/E ratio. The company prioritized growth over profitability, reinvesting its earnings into expansion. Over time, this strategy paid off, and Amazon became one of the most valuable companies in the world.
Investor Sentiment and Negative P/E Ratios
Investor sentiment plays a big role in how negative P/E ratios are perceived. Some investors see it as a sign of trouble, while others view it as an opportunity. The key is to look beyond the numbers and understand the underlying reasons.
For example, if a company is losing money due to poor management, investors might be hesitant to invest. On the other hand, if the company is investing in growth, investors might be more willing to take the risk.
Factors Influencing Investor Sentiment
Here are some factors that influence how investors perceive a negative P/E ratio:
- Management credibility
- Market conditions
- Competitor performance
- Long-term growth potential
How to Invest in Companies with Negative P/E Ratios
Investing in companies with negative P/E ratios can be risky, but it can also be rewarding. Here are a few tips to help you make a more informed decision:
1. Do Your Research: Before investing, make sure you understand the company’s business model, financials, and growth strategy. Don’t just rely on the P/E ratio.
2. Diversify Your Portfolio: Never put all your eggs in one basket. Diversifying your investments can help mitigate risks.
3. Keep an Eye on Market Trends: Stay updated on industry trends and market conditions. This can help you spot opportunities and avoid potential pitfalls.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Here are some common pitfalls to avoid when investing in companies with negative P/E ratios:
- Overlooking red flags
- Ignoring industry trends
- Getting caught up in hype
Conclusion: What Does Negative Price to Earnings Ratio Mean?
So, there you have it—a comprehensive guide to understanding negative price to earnings ratios. While a negative P/E ratio can be concerning, it’s not always a dealbreaker. It all depends on the context and the company’s long-term potential.
Here’s a quick recap:
- A negative P/E ratio happens when a company’s earnings are negative.
- It can be caused by various factors, including one-time events or growth investments.
- Investor sentiment plays a big role in how it’s perceived.
- Doing your research and diversifying your portfolio can help mitigate risks.
Now that you’re armed with this knowledge, it’s time to put it into practice. Whether you’re an experienced investor or just starting out, understanding the nuances of financial metrics like the P/E ratio can help you make smarter decisions.
So, what are you waiting for? Dive into the world of investing and discover the opportunities that await. And remember, knowledge is power!
Table of Contents
- What Exactly is Price to Earnings Ratio?
- Why Does a Negative P/E Ratio Happen?
- Is a Negative P/E Ratio Always Bad?
- How to Interpret a Negative P/E Ratio
- Real-World Examples of Negative P/E Ratios
- Investor Sentiment and Negative P/E Ratios
- How to Invest in Companies with Negative P/E Ratios
- Conclusion: What Does Negative Price to Earnings Ratio Mean?
PricetoEarnings Ratio What Does a High P/E Ratio Mean? Dividend

WHAT DOES PRICE EARNINGS RATIO MEAN?
Price to Earnings Ratio Accounting Play