Is Negative P/E Ratio Good? Unlocking The Mystery Behind This Controversial Metric
Ever wondered if a negative P/E ratio is actually a good thing? Let’s dive right into it, because this topic can get pretty wild and confusing. Imagine you’re scrolling through stock reports or financial news, and you come across a company with a negative P/E ratio. Your first thought might be, “What the heck does that mean?” Don’t worry, you’re not alone. A negative P/E ratio is like the financial version of a mystery box—some people see it as an opportunity, while others run for the hills. But is it really that bad? Or could it be secretly awesome?
Before we go full throttle, let’s break it down. A negative P/E ratio happens when a company reports net losses instead of profits over a specific period. It’s like showing up to a race without a car—sure, you’re there, but you’re not exactly moving forward. However, in the world of finance, things aren’t always black and white. Sometimes, a negative P/E ratio can signal potential for growth or strategic investments that might pay off big time in the future.
Now, if you’re scratching your head wondering why anyone would consider a negative P/E ratio good, buckle up. We’re about to take you on a journey through the ins and outs of this financial metric, exploring its pros, cons, and everything in between. By the end of this article, you’ll have a clearer understanding of whether a negative P/E ratio is worth your attention—or your investment dollars.
- Shubhashree Sahu Mms The Story That Everyones Talking About
- Lara Rose Leak The Untold Story Behind The Viral Sensation
Understanding the Basics of P/E Ratio
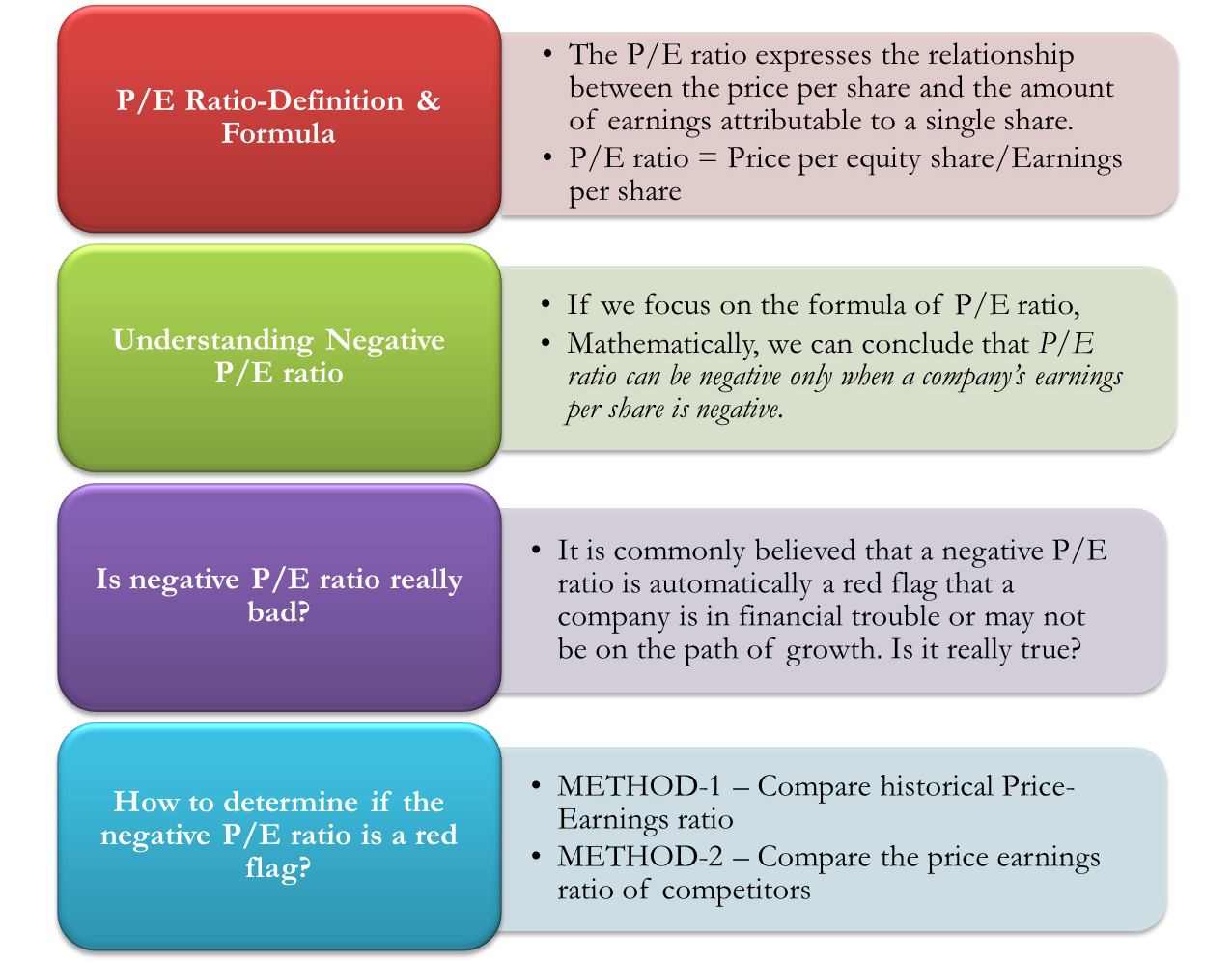
First things first, let’s talk about what a P/E ratio actually is. The Price-to-Earnings (P/E) ratio is like the financial version of a report card—it tells you how much investors are willing to pay for every dollar of a company’s earnings. It’s calculated by dividing the current market price of a stock by the company’s earnings per share (EPS). If a company has a high P/E ratio, it usually means investors are optimistic about its future growth. On the flip side, a low P/E ratio might indicate undervaluation—or potential trouble ahead.
But here’s where things get interesting. When a company reports net losses, its earnings per share (EPS) becomes negative. And since you can’t divide by zero (or a negative number in this case), the P/E ratio flips into the negatives. It’s like trying to solve a math problem where the answer doesn’t exist—or at least doesn’t make sense at first glance.
Why Does P/E Ratio Matter?
Investors love using the P/E ratio because it gives them a quick snapshot of a company’s financial health. Think of it like checking the oil level in your car—it’s not the only thing you need to look at, but it’s definitely important. A healthy P/E ratio can signal strong earnings, solid growth potential, and overall stability. But when that ratio turns negative, it’s like finding a flat tire on your car—it grabs your attention and makes you wonder what went wrong.
- David And Rebecca Muir Wedding Love Story That Captured Hearts Worldwide
- Mikayla Campino Leak The Untold Story You Need To Know About
- P/E ratio helps investors compare companies within the same industry.
- A high P/E ratio might indicate future growth, while a low P/E ratio could signal undervaluation.
- When the P/E ratio becomes negative, it raises red flags—but not always for the wrong reasons.
What Causes a Negative P/E Ratio?
A negative P/E ratio doesn’t just happen overnight. It’s usually the result of a company experiencing financial difficulties, such as net losses or declining revenues. But here’s the twist—sometimes, these losses are part of a larger plan. For example, a company might invest heavily in research and development (R&D) or expansion, which can temporarily dent its earnings. In the short term, this might lead to a negative P/E ratio, but in the long run, it could pay off big time.
Let’s break it down with some common causes:
- Net Losses: If a company reports more expenses than revenues, its earnings per share (EPS) will be negative, resulting in a negative P/E ratio.
- Strategic Investments: Companies often invest in growth opportunities, like expanding into new markets or developing new products. These investments can temporarily reduce profits but boost long-term potential.
- Economic Downturns: During tough economic times, companies may struggle to maintain profitability, leading to negative earnings and, consequently, a negative P/E ratio.
Is a Negative P/E Ratio Always a Bad Sign?
Not necessarily. While a negative P/E ratio might raise eyebrows, it’s not always a death sentence for a company. In fact, some of the most successful businesses started with negative P/E ratios before turning things around. Think about Amazon in its early days—years of losses eventually turned into massive profits as the company dominated the e-commerce space.
So, how do you know if a negative P/E ratio is a warning sign or a hidden gem? It all comes down to context. You need to look beyond the numbers and analyze the company’s overall strategy, market position, and growth prospects. Sometimes, a negative P/E ratio is just a temporary blip on the radar, while other times, it might signal deeper issues.
Benefits of a Negative P/E Ratio
Believe it or not, there are situations where a negative P/E ratio can actually be a good thing. Let’s explore some potential benefits:
- Growth Opportunities: Companies with negative P/E ratios might be investing heavily in expansion, innovation, or market penetration. These investments can lead to significant growth in the future.
- Undervaluation: A negative P/E ratio might indicate that a company is currently undervalued by the market. If its fundamentals are strong, it could be an excellent opportunity for investors to buy low and sell high.
- Strategic Planning: Some companies intentionally operate at a loss in the short term to gain a competitive edge in the long term. For example, they might undercut competitors on pricing to capture market share.
Of course, these benefits aren’t guaranteed. You’ll need to dig deeper into the company’s financial statements, management strategy, and industry trends to determine if a negative P/E ratio is truly a good sign.
When Is a Negative P/E Ratio Worth Considering?
Here’s the million-dollar question: when should you consider investing in a company with a negative P/E ratio? The answer lies in understanding the company’s business model, competitive landscape, and growth trajectory. If the company has a solid plan for turning losses into profits, it might be worth taking a chance. On the other hand, if the losses seem unsustainable or the company lacks a clear path forward, it might be best to steer clear.
Risks Associated with Negative P/E Ratios
While a negative P/E ratio isn’t always bad, it does come with its fair share of risks. Here are some potential dangers to watch out for:
- Sustainability Issues: If a company consistently reports losses without a clear plan for profitability, it might struggle to survive in the long run.
- Market Sentiment: Investors often shy away from companies with negative P/E ratios, which can lead to declining stock prices and reduced investor confidence.
- Financial Instability: Persistent losses can strain a company’s financial resources, making it harder to meet obligations like debt payments or operational expenses.
It’s important to weigh these risks against the potential rewards before making any investment decisions. A negative P/E ratio might seem like a bargain, but if the company can’t turn things around, you could end up losing more than you bargained for.
How to Evaluate a Company with a Negative P/E Ratio
Evaluating a company with a negative P/E ratio requires a combination of quantitative and qualitative analysis. Here are some key factors to consider:
- Revenue Growth: Is the company’s revenue increasing, even if its profits are negative? This could indicate strong demand for its products or services.
- Management Strategy: Does the company have a clear plan for achieving profitability? Look for evidence of strategic investments, cost-cutting measures, or new revenue streams.
- Industry Trends: How does the company’s performance compare to its competitors? Is the entire industry facing challenges, or is the company uniquely affected?
Real-World Examples of Companies with Negative P/E Ratios
To better understand the implications of a negative P/E ratio, let’s take a look at some real-world examples:
Tesla: A Case Study in Growth Over Profitability
Tesla is a great example of a company that has operated with a negative P/E ratio for much of its history. Despite years of losses, Tesla’s stock price soared as investors bet on its potential to dominate the electric vehicle market. The company’s focus on innovation, brand loyalty, and long-term growth strategies eventually paid off, turning it into one of the most valuable automakers in the world.
Uber: Betting on Scale and Market Dominance
Uber is another example of a company that embraced losses in pursuit of market dominance. By offering competitive pricing and expanding into new markets, Uber managed to capture a significant share of the ride-sharing industry. While its negative P/E ratio raised concerns among some investors, others saw it as a sign of aggressive growth and strategic planning.
Conclusion: Is a Negative P/E Ratio Good or Bad?
So, is a negative P/E ratio good or bad? The answer, as with most things in finance, depends on the context. While a negative P/E ratio can signal financial difficulties, it can also indicate potential for growth and strategic investments. The key is to look beyond the numbers and analyze the company’s overall health, strategy, and market position.
Before investing in a company with a negative P/E ratio, ask yourself these questions:
- Does the company have a clear path to profitability?
- Is its revenue growing despite the losses?
- Does it have a competitive advantage in its industry?
If the answers to these questions are positive, a negative P/E ratio might just be the hidden gem you’ve been looking for. But if the company lacks a solid plan or faces insurmountable challenges, it might be best to pass on the opportunity.
Now that you’ve got the lowdown on negative P/E ratios, it’s time to put your newfound knowledge into action. Share your thoughts in the comments below, and don’t forget to check out our other articles for more insights into the world of finance. Happy investing!
Table of Contents
- Understanding the Basics of P/E Ratio
- What Causes a Negative P/E Ratio?
- Benefits of a Negative P/E Ratio
- Risks Associated with Negative P/E Ratios
- Real-World Examples of Companies with Negative P/E Ratios
- How to Evaluate a Company with a Negative P/E Ratio
- Conclusion: Is a Negative P/E Ratio Good or Bad?
- Subhashree Sahu Xxx Debunking Myths And Exploring The Truth
- Marie Temara Nudes Debunking The Viral Sensation And Setting The Record Straight

PricetoEarnings Ratio Negative PE Ratio Is Good Or Bad?
Negative P/E Ratio Really a Red Flag?

NEGATIVE PE RATIO What to Do with These Stocks?