AWS SSH Tunnel: Your Ultimate Guide To Secure Connections
Ever wondered how to establish a secure connection between your local machine and AWS resources? AWS SSH tunnel is the answer you're looking for. This powerful tool allows you to create encrypted channels, ensuring your data stays safe while traversing the internet. Whether you're a developer, system admin, or just someone curious about cloud security, this guide has got you covered.
Imagine this—you're working on a project that requires accessing sensitive data stored in an Amazon EC2 instance. You want to make sure no one intercepts your communication. That's where AWS SSH tunnels come in handy. They act like a secret passageway, protecting your data from prying eyes.
Now, before we dive deep into the nitty-gritty details, let me assure you that this guide isn't just another boring tech article. We'll keep things conversational, breaking down complex concepts into bite-sized pieces. By the end of this, you'll have all the knowledge you need to set up and manage AWS SSH tunnels like a pro.
- Unveiling The World Of Diva Flawless Xxx Video A Comprehensive Guide
- Anjali Arora Mms Video The Untold Story And Facts You Need To Know
What Exactly Is an AWS SSH Tunnel?
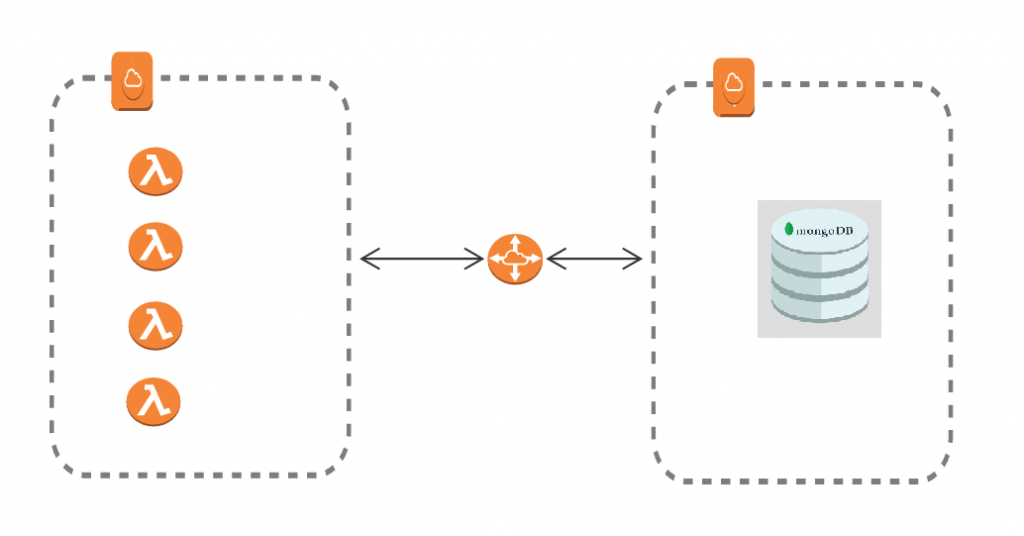
An AWS SSH tunnel is essentially a secure connection between your local computer and an EC2 instance running on Amazon Web Services. Think of it as a virtual hallway that only you and your server can access. The SSH part stands for Secure Shell, which is a protocol designed to encrypt data transmissions over networks.
Let’s break it down a bit more. When you establish an SSH tunnel, you're creating a secure pipe through which data can flow between two points without being tampered with. This is especially useful when dealing with sensitive information like passwords, databases, or private files.
Why Should You Care About AWS SSH Tunnels?
Security is the name of the game here. In today's digital world, data breaches are a real concern. By using AWS SSH tunnels, you significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access to your AWS resources. It’s like putting a lock on your front door—it’s not foolproof, but it sure makes it harder for intruders to get in.
- Lara Rose Onlyfans The Ultimate Guide To Her Journey Content And Impact
- Jameliz Smith The Rising Star In The Adult Entertainment Industry
Here’s a quick list of why AWS SSH tunnels matter:
- Encrypts data transmissions, keeping them private.
- Protects against man-in-the-middle attacks.
- Enables secure access to internal services like databases and web apps.
- Ensures compliance with industry standards and regulations.
Setting Up an AWS SSH Tunnel: Step-by-Step Guide
Alright, let’s roll up our sleeves and get to work. Setting up an SSH tunnel on AWS might sound intimidating, but trust me, it’s easier than you think. Follow these steps, and you’ll be good to go.
Step 1: Gather Your Tools
Before you start, make sure you have everything you need. Here's a quick checklist:
- An AWS account with an EC2 instance up and running.
- An SSH key pair (usually in .pem format) for authentication.
- A terminal or command-line interface on your local machine.
Got all that? Great! Let’s move on to the next step.
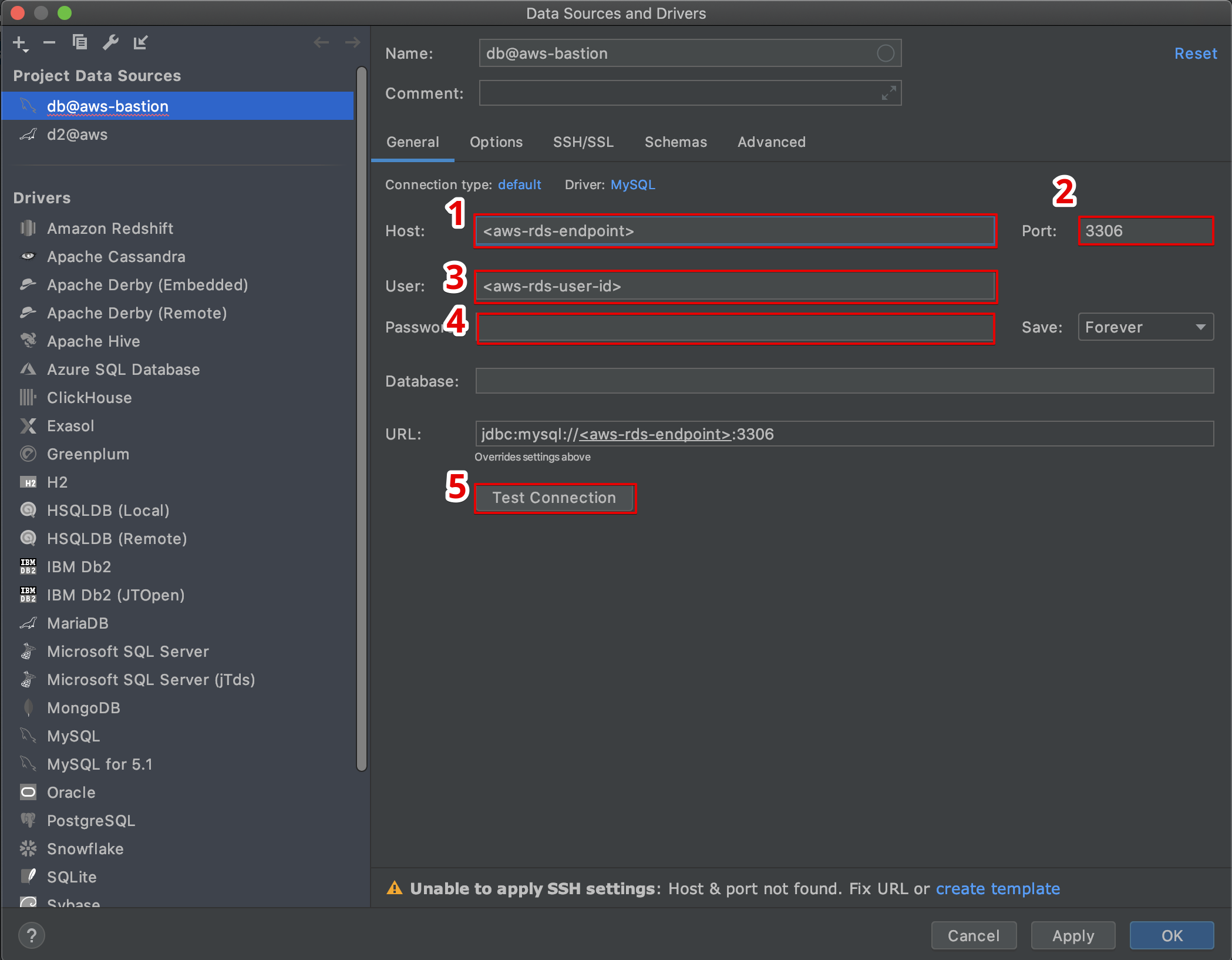
Step 2: Connect to Your EC2 Instance
Using your terminal, connect to your EC2 instance by running the following command:
ssh -i "your-key.pem" ec2-user@your-ec2-public-dns
Replace "your-key.pem" with the path to your private key file and "your-ec2-public-dns" with the public DNS of your EC2 instance. Simple, right?
Step 3: Create the SSH Tunnel
Now comes the fun part—creating the actual tunnel. Use the following command:
ssh -i "your-key.pem" -L local-port:target-host:target-port ec2-user@your-ec2-public-dns
Let’s break it down:
- local-port: The port on your local machine where the tunnel will listen.
- target-host: The internal IP address or hostname of the service you want to access.
- target-port: The port number of the service on the target host.
For example, if you want to access a MySQL database running on port 3306 inside your EC2 instance, you could use:
ssh -i "your-key.pem" -L 3306:localhost:3306 ec2-user@your-ec2-public-dns
Common Use Cases for AWS SSH Tunnels
So, what can you actually do with an AWS SSH tunnel? Quite a lot, actually. Here are some common use cases:
1. Secure Database Access
Imagine you have a MySQL or PostgreSQL database running on your EC2 instance. By setting up an SSH tunnel, you can securely access it from your local machine without exposing it to the public internet.
2. Remote Desktop Connections
Need to access a graphical interface on your EC2 instance? An SSH tunnel can help you set up a remote desktop connection securely.
3. Bypassing Firewalls
Sometimes, corporate firewalls block direct access to certain services. An SSH tunnel can act as a workaround, allowing you to bypass these restrictions while maintaining security.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Even the best-laid plans can go awry. If you run into issues while setting up your AWS SSH tunnel, don’t panic. Here are some common problems and how to fix them:
Problem: Permission Denied (Public Key)
Solution: Make sure your private key file has the correct permissions. Run the following command to fix it:
chmod 400 your-key.pem
Problem: Connection Timeout
Solution: Double-check your EC2 instance's security group settings. Ensure that the necessary ports are open and that your IP address is allowed to connect.
Problem: Tunnel Not Working
Solution: Verify that the service you're trying to access is running on the target host and listening on the correct port. Also, ensure that there are no firewall rules blocking the connection.
Best Practices for Using AWS SSH Tunnels
Now that you know how to set up an SSH tunnel, let’s talk about best practices to keep your connections secure:
- Always use strong, unique passwords for your EC2 instances.
- Limit access to your EC2 instances by specifying allowed IP addresses in security groups.
- Regularly update your SSH clients and servers to patch vulnerabilities.
- Monitor your SSH logs for suspicious activity.
Advanced Techniques: Port Forwarding and Dynamic Tunnels
Once you’ve mastered the basics, you can explore more advanced techniques like port forwarding and dynamic tunnels. These methods offer even more flexibility and control over your SSH connections.
Port Forwarding
Port forwarding allows you to redirect traffic from one port to another. For example, you could forward traffic from your local machine's port 8080 to port 80 on your EC2 instance, enabling you to access a web server securely.
Dynamic Tunnels
Dynamic tunnels act like a SOCKS proxy, allowing you to route all your internet traffic through the SSH tunnel. This is particularly useful when working in untrusted networks, such as public Wi-Fi hotspots.
Security Considerations and Best Practices
Security should always be at the forefront of your mind when working with AWS SSH tunnels. Here are some additional tips to keep your connections safe:
- Use multi-factor authentication (MFA) whenever possible.
- Regularly rotate your SSH keys to minimize the risk of compromise.
- Limit the lifetime of SSH sessions to prevent unauthorized access.
- Stay informed about the latest security updates and patches for SSH.
Conclusion: Take Control of Your AWS SSH Tunnels
And there you have it—a comprehensive guide to AWS SSH tunnels. From setting them up to troubleshooting common issues, we’ve covered everything you need to know to keep your AWS resources secure. Remember, security is a continuous process, so always stay vigilant and keep learning.
Now it’s your turn. Try setting up an SSH tunnel on your own and see how it can transform the way you work with AWS. Got any questions or tips of your own? Drop them in the comments below. And if you found this guide helpful, don’t forget to share it with your friends and colleagues.
Stay secure out there, and happy tunneling!
Table of Contents
- What Exactly Is an AWS SSH Tunnel?
- Why Should You Care About AWS SSH Tunnels?
- Setting Up an AWS SSH Tunnel: Step-by-Step Guide
- Common Use Cases for AWS SSH Tunnels
- Troubleshooting Common Issues
- Best Practices for Using AWS SSH Tunnels
- Advanced Techniques: Port Forwarding and Dynamic Tunnels
- Security Considerations and Best Practices
- Conclusion: Take Control of Your AWS SSH Tunnels
- Oxleak Uncovering The Hidden World Of Digital Security And Privacy
- Unveiling The Truth About Mmsdose A Comprehensive Guide
Aws ssh tunnel milomini
Aws ssh tunnel holopez

Aws ssh tunnel holopez